HEALTHY MOUTH TIPS
Bleeding Gums: A Big Red Flag
[ssba]
Bleeding Gums: A Big Red Flag
While most people tend to be concerned when they see blood, there are thousands of adults in the U.S. whose gums bleed every day – and they aren’t paying any attention to this huge red flag.
In fact, in a study conducted in 1999 at the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), researchers found that 50% of adults in the United States are affected by bleeding gums, and many are not doing anything about it.
 Picture: Shutterstock |
What Does it Mean When Your Gums Bleed?
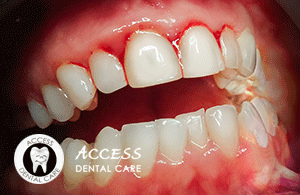
If your gums are swollen and bleeding, this is a sign that you may have a bacterial infection in the gums. If the condition is left untreated, the infection may spread to the periodontal ligament and the underlying bone tissue, damaging the structures that hold your teeth in place and connect your teeth to the jawbone.
In its earliest stage, periodontal disease is known as gingivitis. During this phase, the infection affects primarily the gums, and the presence of harmful bacteria is indicated by swelling and bleeding in the gums upon contact. As periodontal disease progresses, all of the tissues surrounding the teeth become affected, and damage to the teeth, gums, and bone may become severe.
This condition causes pockets to develop around the teeth, which in turn causes the teeth to become loose, and eventually, the teeth may either fall our or they may have to be extracted.
Gum disease is also called periodontal disease, from the Greek “Perio” which means “around” and “dontal” which means “tooth.” Periodontal disease refers to infections affecting the structures that surround the teeth, including the gums, the periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone.
What Are the Causes of Gum Disease?
Periodontal disease is caused by the accumulation of harmful bacteria in dental plaque, a sticky substance that forms on the teeth regularly as a consequence of chewing food. In an attempt to fight the bacterial infection, the body’s immune system releases chemical substances that produce inflammation and wreak havoc on the gums, periodontal ligament, and/or alveolar bone.
Symptoms of gum disease include swollen gums that may or may not be painful, and typically bleed on contact. As the disease progresses, symptoms may include loose teeth, painful abscesses, and profuse bleeding of the gums.
Treatment and Prevention of Gum Disease
It is imperative to brush and floss regularly, practice good oral hygiene, and have regular dental checkups at least once every six months in order to prevent periodontal disease.
Proper brushing and flossing may help keep the plaque that forms on your teeth under control, but you will also need regular professional dental cleanings in order to control the formation of plaque in places that are harder to reach with a toothbrush or dental floss.
The accumulation of plaque below the gum line is especially dangerous, as it will continue to multiply and spread to the periodontal ligament, and underlying bone tissue. This is why regular dental checkups accompanied by professional cleanings are so crucial to preventing the advancement of gum disease.
 Picture: Freepik |
How Does Gum Disease Affect General Health?
More and more, gum disease is being linked to a variety of other health problems. While studies have turned up evidence of the connection between gum disease and various other medical problems, more research is still warranted in this area.
Still, scientists have discovered evidence of a connection between gum disease and certain medical conditions, including the following diseases:
Heart disease — A link has been established between gum disease and conditions such as clogged arteries and heart disease. Scientists also believe that the presence of periodontal disease exacerbates existing heart disease.
Stroke — Periodontal disease is believed to increase the risk of certain types of stroke that are the result of clogged arteries.
Diabetes — It has been found that diabetic patients who also have periodontal disease have more difficulty controlling their blood sugar than their diabetic counterparts not affected by gum disease.
Respiratory disease— Periodontal disease is believed to contribute to lung infections due to the transference of bacteria from the mouth to the lungs.
Premature births – A study conducted in 1996 discovered a relationship between mothers with periodontal disease and delivery of premature infants. Periodontal disease affects up to 90% of the adult population and has been demonstrated to occur more frequently in pregnant women.
If you’d like to know more about how to prevent periodontal disease and maintain healthy teeth and gums, contact Access Dental Care, where Dr. Terry Song provides comprehensive family dentistry for patients in Reno, Sparks, and surrounding communities in Nevada.
